OECD GLP Data Integrity guidelines
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) issued the latest GLP guideline 2016 GLP Data Integrity Advisory document in September 2021 ( Advisory Document n° 22 ). This document provides guidance on how to ensure the integrity of data generated in GLP studies and may highlights challenging situations for the pharma companies impacted by these regulations.
This advisory document is related to the GLP guideline already published in 2016, intending, more broadly, to provide a framework for conducting non-clinical laboratory studies that support the safety and efficacy of chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and other products.
Additionally to this guideline, several GLP Consensus and Advisory Documents are provided to focus on different specific topics, and to detailed what is expected from Pharma companies in term of control and documentation. The GLP Data Integrity is one of these.
The key highlights of the 2021 OECD GLP guideline include:
- Scope: The guideline applies to non-clinical safety studies conducted on pharmaceuticals, pesticides, chemicals, and other products.
- Principles: The guideline outlines the principles of GLP, which include the need for a quality system, the importance of documentation and record keeping, and the necessity for standard operating procedures (SOPs) and validation procedures.
- Management: The guideline requires that management be responsible for ensuring compliance with GLP and that they provide adequate resources for implementing GLP.
- Facilities: The guideline outlines the requirements for facilities used in non-clinical studies, including the need for suitable premises, equipment, and environmental controls.
- Study Conduct: The guideline requires that studies be conducted according to the study plan and SOPs, and that all data be recorded and maintained in a traceable and auditable manner.
- Quality Assurance: The guideline outlines the requirements for a quality assurance program, which includes the need for audits, inspections, and reviews of study data and reports.
- Personnel: The guideline requires that personnel be adequately trained and qualified for the tasks they are performing.
Overall, the 2016 OECD GLP guideline provides a comprehensive framework for conducting non-clinical laboratory studies. Its emphasis on data integrity and the importance of quality systems make it an essential tool for pharmaceutical companies seeking to ensure the safety and efficacy of their products.
In addition to the above highlights, the GLP Data Integrity advisory document provides guidance on how to ensure the integrity of data generated in GLP studies. Some key points of the advisory document include:
- The importance of data integrity: The document emphasizes the importance of data integrity in GLP studies to ensure that the data is reliable, accurate, complete, and consistent.
- Definition of data integrity: The advisory document defines data integrity as the "extent to which all original records and true copies are complete, consistent, accurate, reliable, and that all changes are fully documented." (ALCOA+ Principles)
- Roles and responsibilities: The document outlines the roles and responsibilities of various personnel involved in GLP studies, including management, study directors, quality assurance personnel, and analysts.
- Data management systems: The advisory document provides guidance on data management systems, including the need for secure storage, backup systems, and data retrieval procedures.
- Documentation: The document emphasizes the need for complete documentation of all activities related to the study, including procedures, protocols, data collection, and analysis.
- Quality assurance: The advisory document emphasizes the need for a comprehensive quality assurance program to ensure that all activities related to the study are conducted in accordance with GLP regulations.
- Training: The document emphasizes the need for personnel involved in GLP studies to receive appropriate training on GLP principles, including data integrity.
In summary, the advisory document provides detailed guidance on how to ensure the integrity of data generated in GLP studies, including specific recommendations for data management systems, documentation, quality assurance, and training. Adherence to these principles will help to ensure that the data generated in GLP studies is reliable, accurate, and consistent, which is critical for the safety and efficacy of regulated products.
Pharmaceutical companies are expected to adhere to these guidelines in order to ensure the safety and efficacy of their products. Failure to comply with GLP can result in the rejection of data by regulatory agencies, delays in product approval, and potentially costly recalls or litigation.
Which differences between the OECD guide line for Good laboratory practices and the Good Manufacturing Practices from EMA ?
Here are some key similarities and differences between the two guidelines:
- Scope: The OECD GLP guideline focuses on the conduct of non-clinical safety studies, while the EMA GMP guideline focuses on the manufacture and control of medicinal products for human use. While the two guidelines have different scopes, they share some common elements related to quality management, documentation, and data integrity.
- Regulatory basis: The OECD GLP guideline is a non-binding guidance document, while the EMA GMP guideline has the force of law within the European Union. Compliance with the GMP guideline is mandatory for companies seeking to market medicinal products in the EU.
- Applicability: The GLP guideline applies to all non-clinical safety studies conducted to support the safety assessment of chemicals, while the GMP guideline applies to all phases of the manufacturing process for medicinal products, from the sourcing of raw materials to the release of finished products.
- Requirements: The GLP guideline provides guidance on the organization and management of non-clinical studies, including requirements for facilities, equipment, personnel, and documentation. The GMP guideline provides detailed requirements for the manufacture and control of medicinal products, including requirements for quality management systems, documentation, validation, and auditing.
- Data integrity: Both guidelines place a strong emphasis on data integrity and require companies to have measures in place to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of data generated during non-clinical or clinical studies. The guidelines also require companies to document their data management practices and to maintain data for a specified period of time.
While the OECD GLP guideline and the EMA GMP guideline have different scopes and regulatory bases, they share some common elements related to quality management, documentation, and data integrity. Companies in the pharmaceutical industry must comply with both guidelines to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of their products.
biomedion GmbH is a dynamic, international organization that provides cloud-based data archiving solutions since 2011 to organizations across the world. As a forward-thinking technology company, biomedion stands out from the crowd by delivering innovative solutions that allow its customers to securely store and access their data in a GxP compliant manner.
biomedion has developed neuronOS, focused on Data Integrity management, to bring pharmaceutical companies into compliance with these regulations (GMP and GLP). This platform is able to handle the complete data lifecycle, from the capture of the raw data until the end of the archive retention schedule.
Example of data lifecycle - Processing and file format conversion steps are not managed by neuronOS:
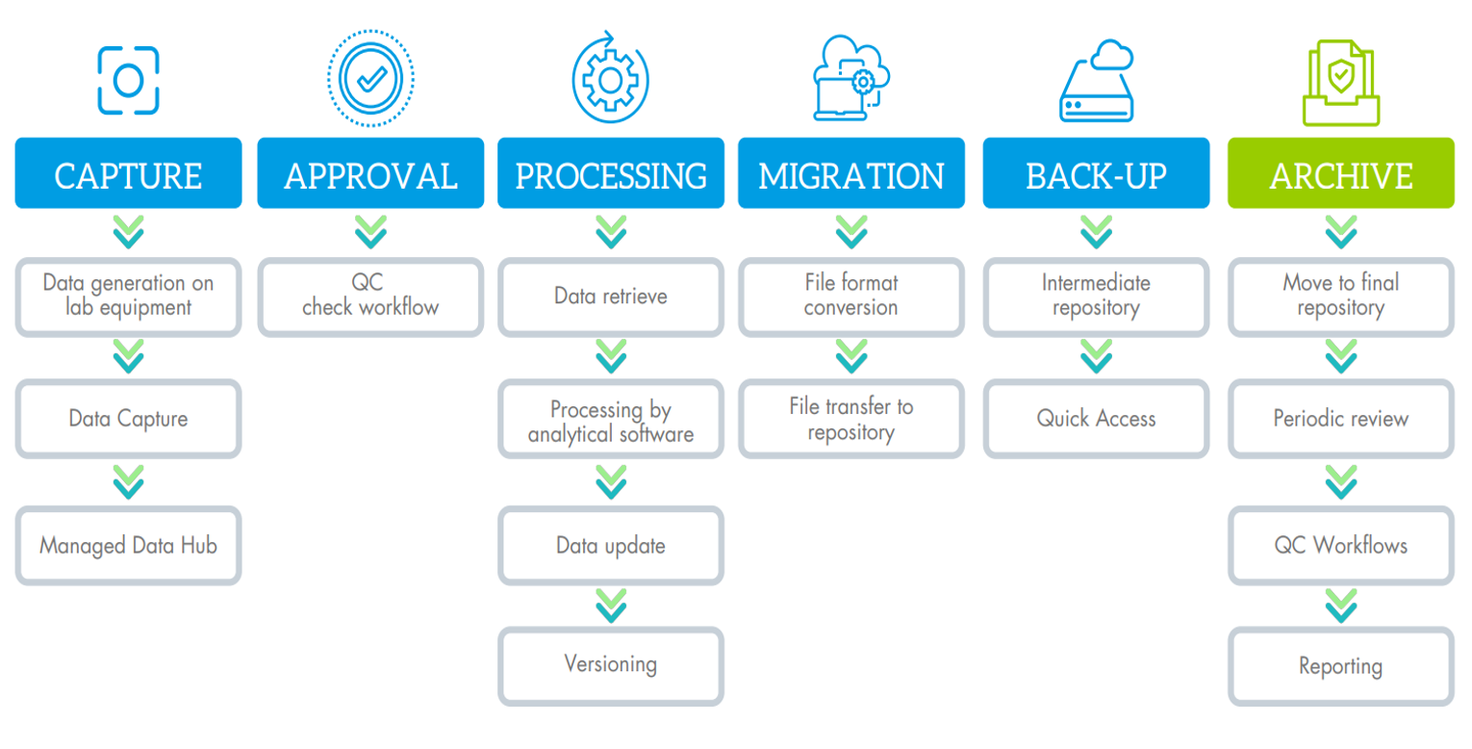
Even if the data capture itself is probably the most challenging step in the whole process (See boxed text ), due to diversity of file types and instrument processes, the complete workflow can be monitored, controlled, and overseen by neuronOS.
We developed a dedicated agent for the capture called WATCH+, which is completely configurable according to the specific working process of each lab equipment, in such a way, that the data can be captured and secured as soon as it is released by the software of your device. You can design your quality control or approval workflow to ensure the right data management according to your internal procedures.
As soon as the data is captured, any status change, action, migration, quality check done on your data is tracked and logged in an audit trail, ensure the complete traceability and history about what is done with your data.
Data storage flow:
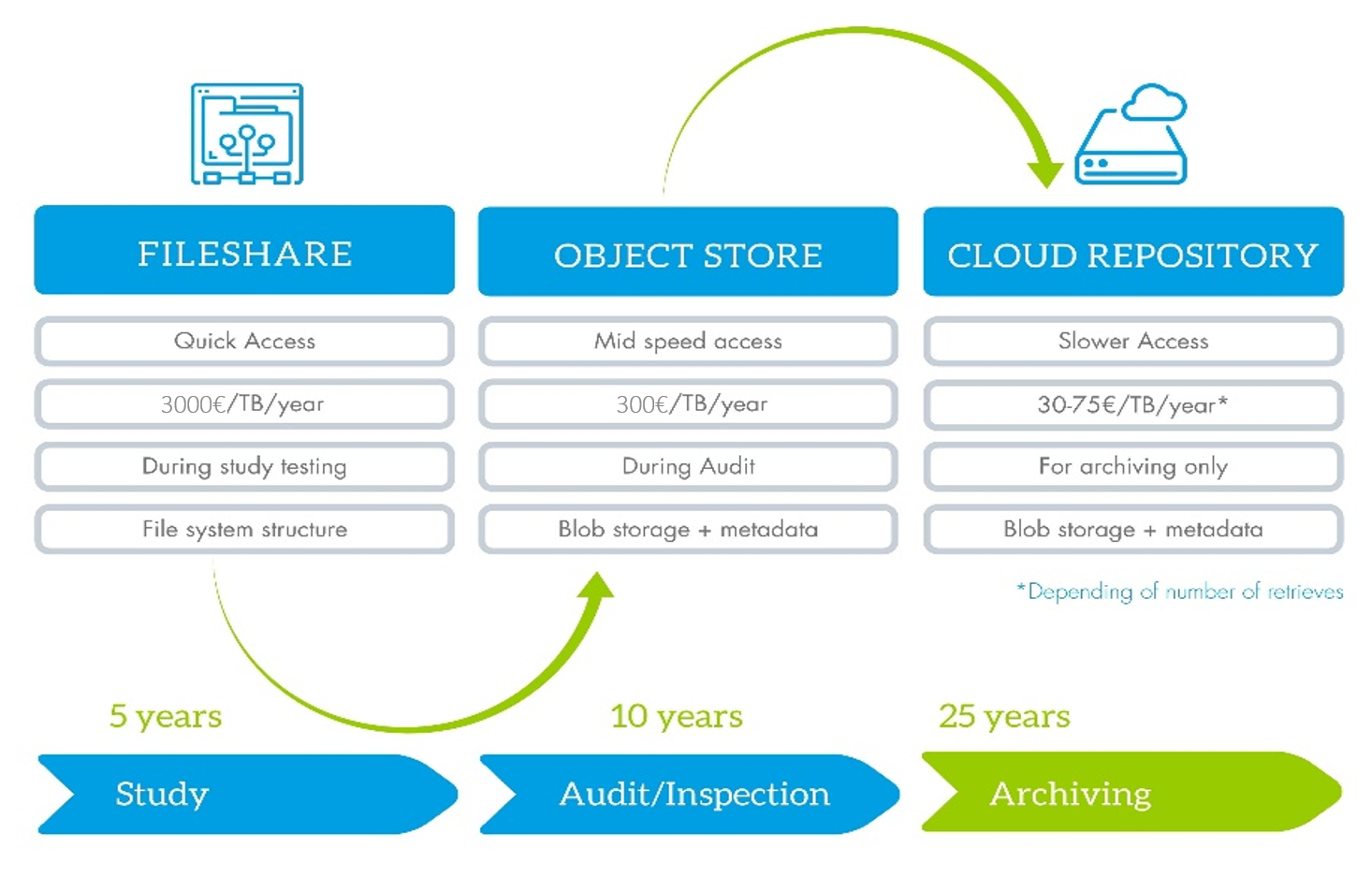
Accessibility of data is one of the key advantage of neuronOS. The scientist can access the data, wherever he is thanks to the full cloud (platform and data in the cloud) or hybrid (platform in the cloud and data on premises) configuration capability of the platform. Whenever it’s needed you can access your data for calculation, review, comparison, download, without any delay, to allow you to take the most appropriate decision at the right time.
To make the total cost of ownership of your data more efficient, it makes sense to migrate your data to a lower cost storage solution, such as a cold cloud storage or a glacier. With neuronOS, you can schedule this migration (e.g. at the end of a study) to migrate the data to a storage dedicated to archiving, where you don’t need to access the data anymore, only in case of audit, as the download of data is the most expensive with cloud storage solutions. Everything is controlled, with data integrity check before and after the migration and all along the archiving period, on which you can report to ensure that the process have been well executed and the data are still safe.
Overall, neuronOS can bring you compliant with the regulations applied to Pharma companies, in GLP and GMP environments. This platform will help you to face the major challenges in data management, where it can store any kind of files, the solution is scalable thanks to it’s cloud agnostic architecture, the data management process is automated as much as possible reducing the risk of errors, the data are secured and keep private (storage in private cloud), each step of the process is controlled and logged and you can reduce the storage cost of your huge amount of data.
Data capture and regulatory compliance. What are the key challenges?
- Complexity of regulations: The regulatory environment for pharmaceuticals is complex and constantly evolving. Companies must stay up to date with changing regulations and ensure that their data capture processes comply with the latest guidelines. This can be time-consuming and requires specialized expertise.
- Lack of standardization: There is a lack of standardization in data capture across the industry, due to the diversity of devices and suppliers, which can make it difficult to compare data across studies or to ensure that data is captured in a consistent and reproducible manner.
- Volume and diversity of data: The volume and diversity of data generated by laboratories and manufacturing can be overwhelming, making it difficult to ensure that all relevant data is captured and properly documented.
- Risk of errors and omissions: Data capture errors and omissions can have serious consequences, including delays in product approval or even regulatory action. Pharmaceutical companies must have robust quality control processes in place to minimize the risk of errors, avoid manual interventions (manual copy/paste, use of external devices,…) and ensure the integrity of the data.
- Data security and privacy: The sensitive nature of pharmaceutical data means that it must be stored and transmitted securely to ensure compliance with data privacy regulations.
- Training and resource constraints: Effective data capture requires specialized training and expertise, as well as sufficient resources to support data capture processes. Pharmaceutical industries must ensure that their employees are adequately trained and that they have the necessary resources to support compliance with data capture regulations.
Data capture for regulatory compliance can be a complex and challenging process. To minimize pain points, companies must stay up to date with changing regulations, standardize data capture processes everywhere it is possible, implement robust quality control processes, ensure data security and privacy, and provide adequate training and resources to support their data capture efforts.
ALCOA+ Principles
These principles are a set of guidelines for the responsible use and management of data in pharmaceutical environment.
- Attributable: All data should be linked to the person or group responsible for its collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Legible: Data should be recorded in a clear, understandable, and permanent manner.
- Contemporaneous: Data should be recorded in real-time as the study is being conducted, or as soon as possible afterward.
- Original: The original data should be preserved and maintained, rather than relying on copies or summaries.
- Accurate: Data should be free from errors or bias, and should accurately reflect the observed or measured values.
- Complete: All data relevant to the research question should be collected and recorded, including negative or inconclusive results.
- Consistent: Data should be collected and recorded in a consistent manner, using standardized procedures and definitions.
- Enduring: Data should be stored in a secure and accessible manner, with proper backups and protections against loss or damage.
- Available: Data should be made available to other researchers, subject to appropriate protections for confidentiality and privacy.
Sources
Good laboratory practice compliance | European Medicines Agency (europa.eu)
OECD Series on Principles of Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) and Compliance Monitoring - OECD
